- Published on
Streaming data in Next.js using API route
- Authors
- Saad Bash
Define a simple GET route in /app/api which will stream some sample data.
// File: /app/api/route.js
export function GET() {
const responseStream = new TransformStream()
const writer = responseStream.writable.getWriter()
let i = 1
const interval = setInterval(() => {
writer.write(JSON.stringify({ message: `Hello ${i}` }) + '\n\n')
i++
if (i === 11) {
clearInterval(interval)
writer.close()
}
}, 500)
return new Response(responseStream.readable, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'text/event-stream',
Connection: 'keep-alive',
'Cache-Control': 'no-cache, no-transform',
},
})
}
Here GET() method creates a server-sent event stream. It sends a series of "Hello" messages (from "Hello 1" to "Hello 10") to the client every 500ms.
The data is sent as a stream using the TransformStream API.
Create a client component that can read the streaming data
// File: /app/page.js
'use client'
import { useState } from 'react'
export default function Home() {
const [log, setLogs] = useState([])
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false)
const handleClick = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
setLoading(true)
try {
const response = await fetch('/api')
const reader = response.body?.getReader()
const decoder = new TextDecoder()
let done = false
while (!done) {
const result = await reader?.read()
if (result?.done) {
break
}
const text = decoder.decode(result?.value, { stream: true })
setLogs((prev) => [...prev, text])
}
setLogs((prev) => [...prev, 'Done ✅'])
} catch (error) {
setLogs((prev) => [...prev, 'An error occurred ❌'])
} finally {
setLoading(false)
}
}
return (
<main>
<h1>Next.js Streaming Example</h1>
<div>
{!log.length && (
<button onClick={handleClick} disabled={loading}>
{loading ? 'Loading...' : 'Click Me!'}
</button>
)}
</div>
<div>{log && log.map((l, i) => <p key={`log-${i}`}>{l}</p>)}</div>
{log.length > 0 && !loading && (
<div>
<button onClick={() => setLogs([])}>Clear logs</button>
</div>
)}
</main>
)
}
In this client component, The handleClick function fetches data from the /api endpoint on button click. It reads the response as a stream, decoding each chunk of data into text and adding it to the log state.
Realtime streaming looks something like this
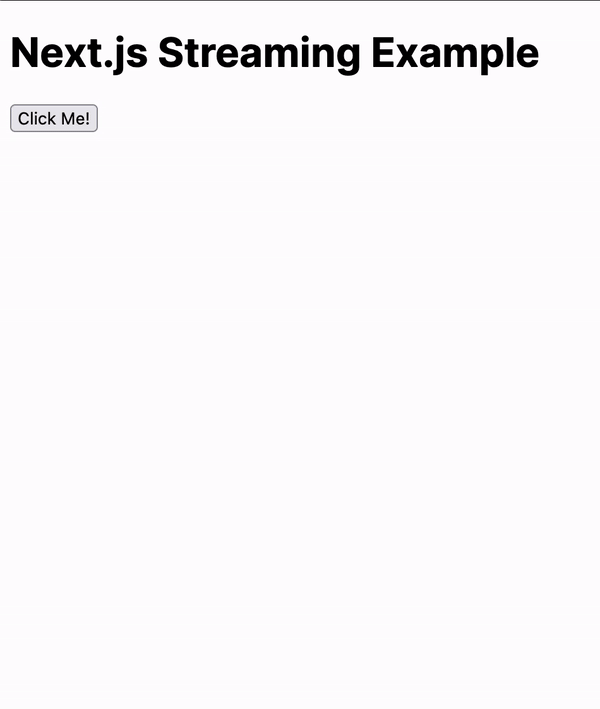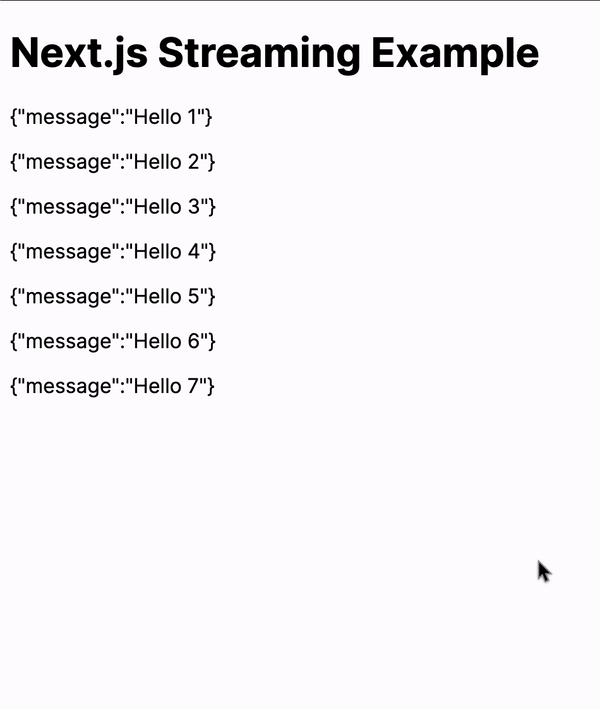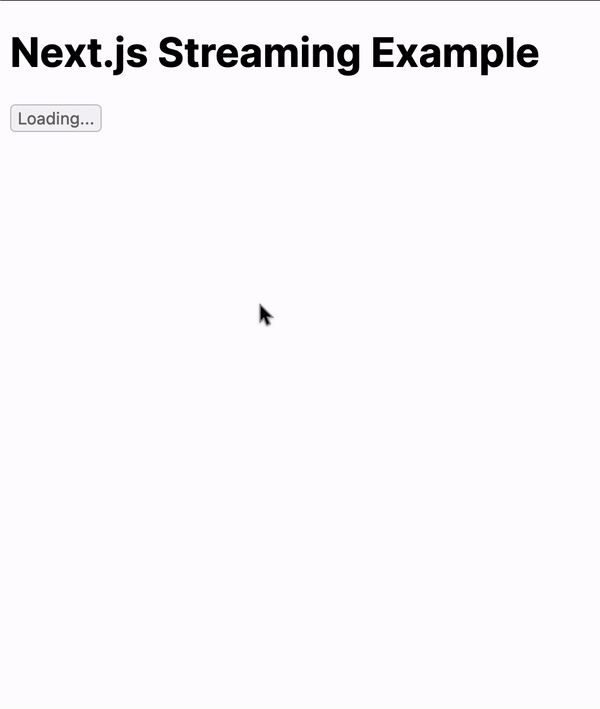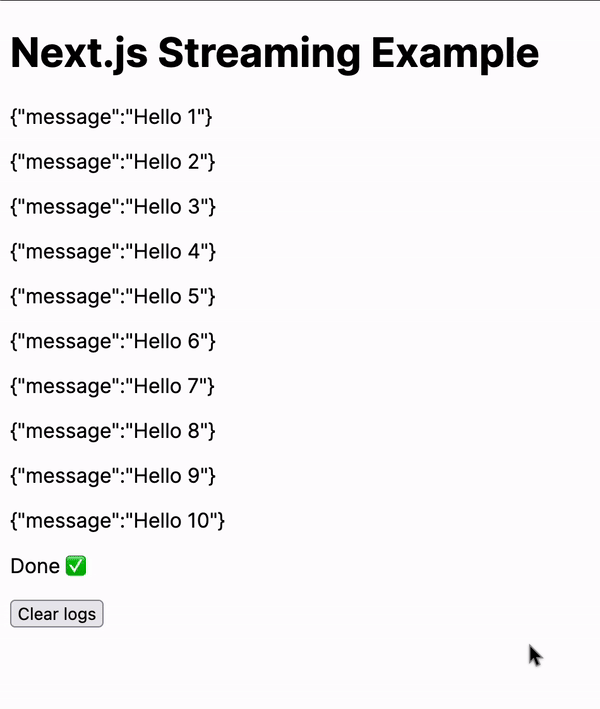
While this example is straightforward, the possibilities with streaming data are virtually endless. You can stream larger datasets, integrate with different APIs, or even build real-time applications.
I hope this article has given you some insight into the power and flexibility of streaming data in Next.js.
Happy Coding!
- Saad Bash